How the cannabis industry can solve its pollution and reduce its carbon footprint - By Dario Sabaghi
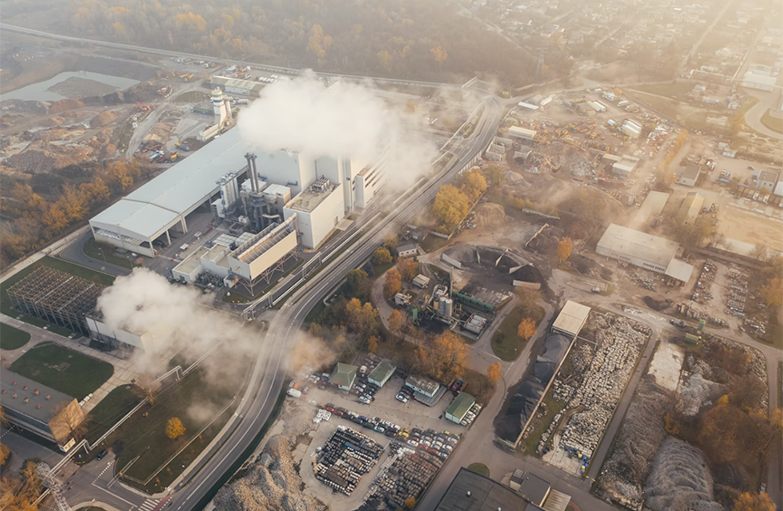

Cannabis is not as green as we imagine, The growing cannabis industry can cause excess pollution like any other industry. As it is part of the agricultural industry, it follows the same dynamics and can generate pollution.
Cannabis is not as green as we imagine. The growing cannabis industry can cause excess pollution like any other industry. As it is part of the agricultural industry, it follows the same dynamics and can generate pollution.
Although the cannabis industry is in the early stage of its development and transition to becoming a large-scale industry, it is necessary to understand the challenge that it will soon face. In a commitment to fight climate change and find the way for a sustainable economy, the cannabis industry should create an ecosystem suitable for eco-friendly solutions.
To understand the pollution of the cannabis industry, it is necessary to have a glance at the concept of carbon footprint, which relates to the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere resulting from the activities of a particular individual, organization, community product, service and so on.
For instance, the average carbon footprint per person in the UK is 12.7 tons of CO2equivalent per year1, while the average carbon footprint of a smartphone produces around 70 kg CO2 equivalent2.Experts calculate a carbon footprint following several parameters gathered in the life cycle of a product. It is an important instrument to understand the impact of a person’s behaviour on global warming.
The carbon footprint of the cannabis industry is quite high. A study by Colorado State University published in the scientific journal Nature Sustainability shows that one kg of dried flowers produces from 2,283 to 5,184 kg CO2 equivalent3.
Such an amount is due to the electricity production and natural gas consumption from indoor cultivation, helped by high-intensity grow lights and the supply of carbon dioxide for accelerating the plant growth. Cultivating cannabis indoors significantly affects the carbon footprint.
A Global Footprint Network’s analysis4 showed that producing one kilogram of dried cannabis flower per year in an open greenhouse in Colombia has a far lower Ecological Footprint than production at sites in Colorado and Washington. Choosing to grow cannabis indoors or outdoors makes a big difference. Indoor cultivation increases pollution due to the high amount of energy spent on lighting. Outdoor crops are more sustainable than indoor cultivations, but not exempt from generating pollution.
The cannabis industry contributes to pollution in several ways. Indoor cannabis cultivation produces biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) that could contribute to ozone formation and air pollution when reacting to urban air constituents5. Emissions from cannabis growing facilities impact the quality of air because the concentrations of BVOCs and butane contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which is a toxic substance that is harmful to humans to breathe.
Regarding water pollution, experts recognize water contamination from agricultural pesticide use and eutrophication (excessive richness of nutrients) of freshwater as a global problem. So experts think that pollution from the cannabis industry may cause an environmental risk to water quality.
A big part of these issues is due to the illegality of cannabis cultivation around the world. Illegal cannabis growers pose an enormous threat to the ecosystems, as they may divert vast amounts of water to satisfy the needs of cannabis crops. Furthermore, the use of pesticides and chemical nutrients to help grow cannabis faster may harm the environment and the quality of cannabis itself.
As well as water, cannabis waste and electricity, there are other factors that compound the cannabis carbon footprint. One component of the legal industry concerning environmentalists is the packaging. Plastic is the most-used material to sell cannabis dried flowers, while aluminum is widely used for cannabis-infused products. As these materials are faster and cheaper packaging solutions, the cannabis industry is likely to increase pollution.
However, several sustainable solutions could help to mitigate the cannabis carbon footprint.Growing cannabis outdoors would be the best solution for everyone, as it is less harmful to the planet. However, not all cannabis companies have this logistical solution available.
But energy consumption is not the only component of indoor cannabis cultivation that creates environmental problems. Other cultivation practices negatively impact the environment. Using pesticides and synthetic nutrients harm the environment, so growers should use natural strategies for reducing pollution and production costs. Cannabis crops should avoid altering ecosystems, and growers should cultivate cannabis sustainably and avoid negatively effecting the local community.
One of these sustainable solutions can be solved by growing organic cannabis, which means cultivating the cannabis plant as nature intended by utilizing organic soil and natural nutrients.Another strategy to adopt to reduce carbon footprint is rethinking cannabis infrastructures.
Companies should use hemp to build cannabis facilities. Hempcrete is a bio-composite building material made from the internal woody core of the hemp plant, mixed with a lime-based binder. This mixture makes hempcrete a strong building material that helps reduce the carbon footprint of the cannabis industry.
Besides hempcrete buildings, cannabis companies should do everything possible to reduce the amount of energy needed to produce cannabis. Energy power should come from renewable sources. More and more companies are using solar panels to help reduce the need for energy from fossil fuel sources. However, there are other energy resources available, such as wind power and hydropower.
Regarding the packaging of petroleum-based plastics, companies should consider recyclable materials like glass or biodegradable materials. Hemp plastic is also an alternative because it would reduce cannabis waste and have a much-reduced impact on the environment.
As the cannabis industry is growing rapidly, following these and other sustainable strategies and practices can help the sector promote itself as a sustainable economy and attract forward-looking investors. Governments, international institutions, and companies have taken seriously the fight against climate change. Reducing CO2 emissions has become the leitmotif of many industries, including the automotive sector.
In this context, cannabis policies can help combat climate change. As we have seen, illegal cannabis operations harm the environment and increase pollution significantly. However, they won’t stop. Only legalizing cannabis can help guarantee sustainable procedures to produce cannabis to provide the best product with the least impact on the environment.
1 https://www.pawprint.eco/eco-blog/average-carbon-footprint-uk
2 https://honestmobile.co.uk/2020/08/25/whats-the-carbon-footprint-of-my-smartphone/
3 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-021-00691-w
4 https://www.footprintnetwork.org/2017/08/16/ecological-footprint-cannabis/
Written and Published By Dario Sabaghiin Weed World Magazine issue 152
Image: Unsplashed - Marcin Jozwiak











Please complete your information below to login.
Sign In
Create New Account